Understanding Temperature and Humidity Cycles in Climatic Testing
In product qualification and reliability engineering, climatic testing plays a critical role in assessing how materials and components behave under real-world conditions. Among the most effective approaches is cyclic temperature and humidity testing, which simulates environmental fluctuations that products often encounter during their service life.

Constant vs. Cyclic Testing
Traditional climatic tests often use constant temperature and humidity conditions. While this method is useful for basic stability checks, it does not fully reflect the stresses that products face outdoors or in variable indoor environments. Cyclic testing, in contrast, exposes specimens to repeated changes in temperature and humidity. These cycles accelerate failure mechanisms such as thermal expansion, contraction, condensation, and moisture absorption, offering a more realistic picture of long-term performance.
Typical Applications
Automotive electronics: Components are subjected to rapid temperature swings and condensation, especially in under-hood environments.
Aerospace and defense: Avionics and structural materials must withstand extreme thermal cycling during altitude changes.
Pharmaceutical packaging: Stability chambers use humidity cycles to test how packaging materials protect drug formulations.
Building materials: Coatings, insulation, and polymers are exposed to alternating hot, cold, dry, and humid conditions in daily use.
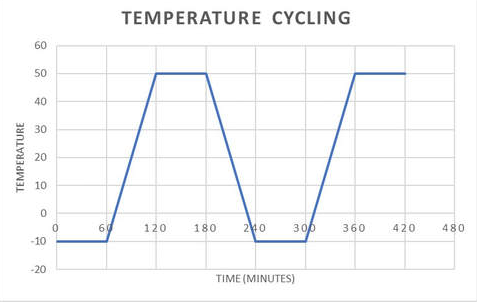
Common Test Cycles
Depending on the standard and the product, test chambers can reproduce different cycles:
High–low temperature cycles with controlled transition rates
Temperature–humidity alternating cycles, often ranging from 20% to 95% relative humidity
Combined stress tests that pair temperature and humidity with vibration or UV exposure
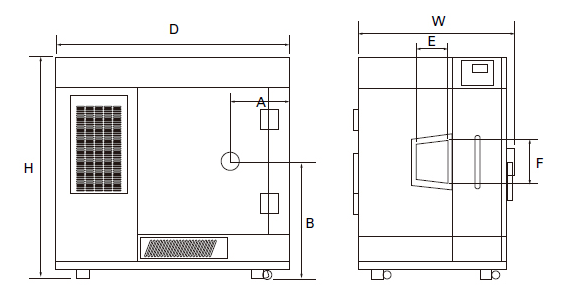
Equipment Considerations
Modern temperature and humidity chambers are designed to deliver precise control over test parameters. Features such as programmable profiles, real-time monitoring, and data logging ensure consistency and compliance with international standards like IEC 60068, MIL-STD-810, and ICH Q1A for pharmaceuticals.
Value for Product Development
By replicating natural fluctuations, cyclic testing helps engineers identify weak points that constant conditions may overlook. Cracking, delamination, corrosion, and electronic failures can emerge earlier, enabling corrective design measures. The result is shorter development cycles, higher product reliability, and greater confidence when entering regulated markets.
Temperature and humidity cycles in climatic testing are more than a laboratory procedure—they are an essential tool for ensuring durability, safety, and compliance. Selecting the right cycle profile depends on the product, its application, and the industry requirements. For manufacturers, understanding these principles is key to delivering products that perform reliably in the environments where they matter most.