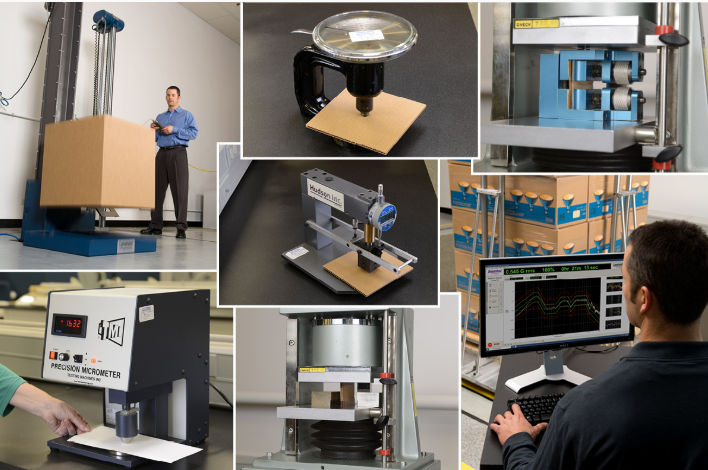
Packaging Reliability Testing: How Drop, Compression, and Transport Simulation Improve Product Safety
In modern supply chains, packaging is not just a container — it’s a protective system that ensures products survive storage, handling, and global transportation. Before mass production, engineers and quality teams relied on packaging tests to evaluate how materials and box designs withstand real-world conditions such as shock, vibration, and stacking pressure.
Why Packaging Reliability Testing Matters
 Every logistics process—whether air, sea, or road—introduces risks of impact, vibration, and compression. A single weak point in packaging can result in product damage, customer complaints, and costly returns. Instead of depending on one-time shipment tests, manufacturers perform standardized lab tests to quantify packaging strength and performance.
Every logistics process—whether air, sea, or road—introduces risks of impact, vibration, and compression. A single weak point in packaging can result in product damage, customer complaints, and costly returns. Instead of depending on one-time shipment tests, manufacturers perform standardized lab tests to quantify packaging strength and performance.
These tests simulate worst-case scenarios consistently, enabling R&D teams to compare materials, optimize packaging design, and ensure compliance with international transport safety standards.
Packaging Test Standards
Several recognized organizations define global testing protocols:
ISTA (International Safe Transit Association) — Includes popular series like ISTA 1A, 2A, and 3A, covering vibration, drop, and compression tests for packaged products.
ASTM D4169 — Defines laboratory simulation for distribution cycles involving shock, vibration, and compression.
ISO 2248 — Specifies drop test methods for filled transport packages.
ISO 2233 / ISO 2872 — Address climatic conditioning and compression testing under controlled humidity and temperature.
These standards guide packaging engineers in evaluating transport stability, cushion performance, and stacking strength before shipping.
Testing Methods and Equipment
Drop Test (Free-Fall Impact Test)
Measures packaging’s ability to absorb impact when dropped during handling.
Equipment: ASLI Drop Test Machine, capable of testing different orientations and heights for accurate repeatability.
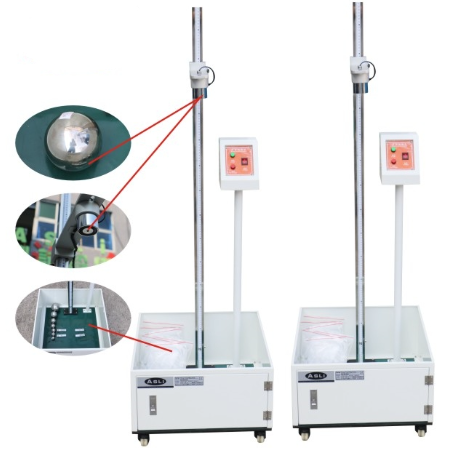

Vibration Test (Transport Simulation)
Simulates vibration during truck or air transport.
Equipment: ASLI Vibration Test Machine, replicating road-induced vibration frequencies from 3 to 200 Hz for realistic motion simulation.

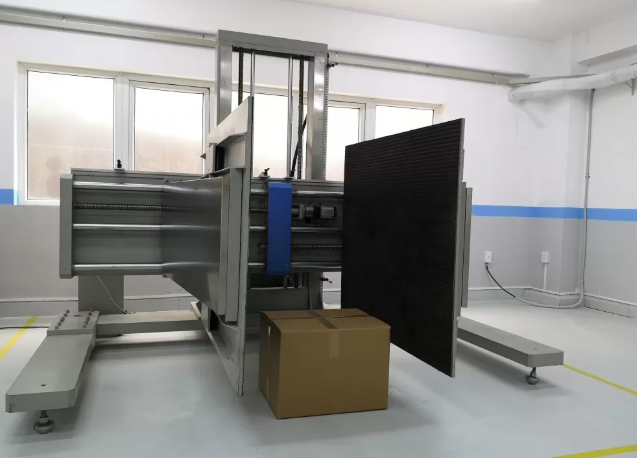
Compression Test
Evaluates box stacking strength under load.
Equipment: ASLI Box Compression Tester, designed to determine maximum load before deformation or collapse.

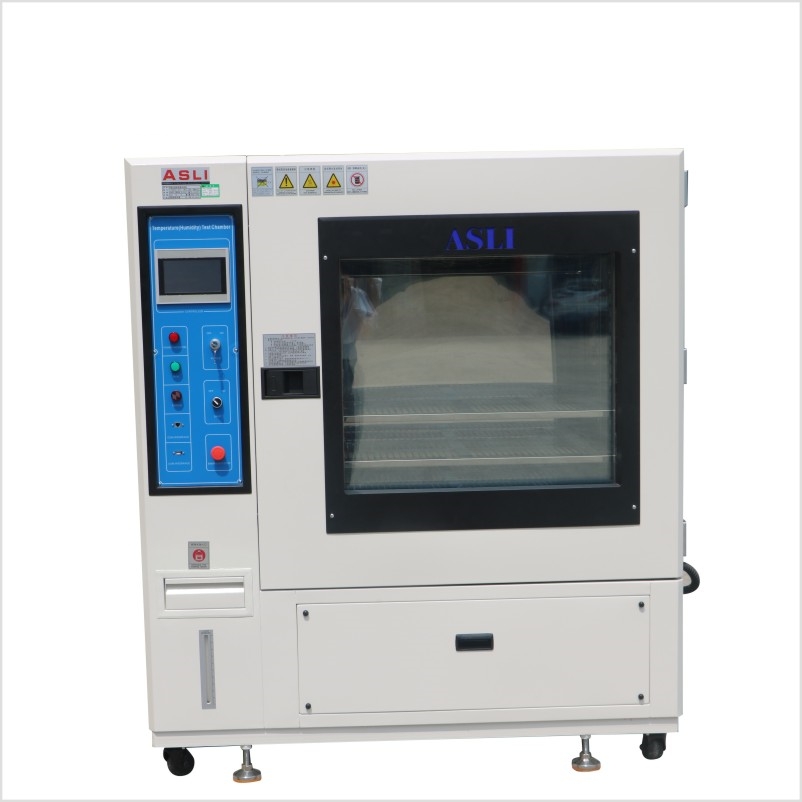
Climatic Conditioning
Packaging often experiences humidity and temperature fluctuations during storage and transport.
Equipment: ASLI Temperature Humidity Chamber, used for pre-conditioning before mechanical tests to simulate real environmental stress.

Why Lab Simulation Is Better Than Field Testing
Real shipment trials are unpredictable and cannot replicate identical conditions. Laboratory simulation offers:
Consistency: Same vibration and drop patterns for every sample.
Speed: Results obtained in hours instead of weeks.
Control: Adjustable parameters such as temperature, humidity, and vibration frequency.
Cost Efficiency: Early identification of design weaknesses before full-scale shipment.

Integrated Packaging Development and Testing
Modern R&D teams integrate packaging testing into product design. For example:
In electronics, engineers test how foam cushioning absorbs energy under repeated drop cycles.
In food and pharmaceutical logistics, humidity chambers verify packaging integrity under temperature cycling conditions.
Automotive component suppliers use transport simulation systems to validate pallet and container robustness for export.
Through continuous testing, packaging transitions from a cost element into a strategic factor in ensuring brand reliability and customer satisfaction.
ASLI Solutions for Packaging Test and Simulation
ASLI provides a full range of environmental and mechanical testing systems that meet ISTA, ASTM, and ISO standards, including:
These instruments support packaging reliability evaluation for industries ranging from consumer electronics to heavy equipment, helping engineers validate every step—from design verification to shipment simulation—with precise and repeatable results.